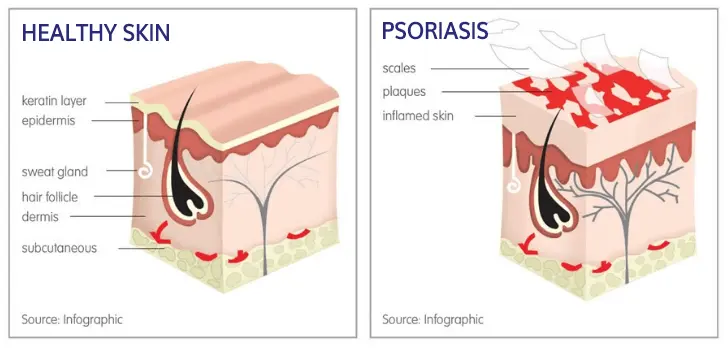
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that causes skin cells to multiply rapidly, leading to red, scaly patches that can be itchy and painful. While the exact cause of psoriasis isn't fully understood, various treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected. Here, we'll explore the best treatment options for psoriasis that have shown efficacy in alleviating symptoms.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are often the first line of defense against psoriasis. These medications are applied directly to the skin and can help reduce inflammation and scaling. Here are some common topical treatments:
- Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory medications are effective in reducing redness and swelling. They come in various strengths, and it's important to use them as directed to avoid side effects.
- Vitamin D Analogues: Calcipotriene and other vitamin D derivatives help slow down skin cell growth and are often used in combination with corticosteroids.
- Retinoids: Topical retinoids like tazarotene can help normalize skin cell production and are beneficial for plaque psoriasis.
- Coal Tar: This traditional treatment helps reduce scaling, itching, and inflammation. It can be messy but is still effective for many individuals.
Phototherapy
Phototherapy involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision. This treatment can be particularly effective for moderate to severe psoriasis. Here are the main types of phototherapy:
- UVB Therapy: Ultraviolet B light can penetrate the skin and is effective in slowing down the rapid growth of skin cells.
- PUVA Therapy: This involves taking a medication called psoralen that makes the skin more sensitive to UVA light, followed by exposure to UVA.
- Excimer Laser: This targeted laser treatment focuses on specific patches of psoriasis, making it a good option for localized areas.
Systemic Treatments
For those with severe psoriasis or those who don't respond to topical treatments, systemic treatments may be necessary. These medications work throughout the body and can include:
- Oral Retinoids: Acitretin is an oral retinoid that reduces skin cell production. It is generally used for severe cases of psoriasis.
- Immunosuppressants: Methotrexate and cyclosporine can help control the immune response that triggers psoriasis, but they require regular monitoring due to potential side effects.
- Biologics: These are newer medications that target specific parts of the immune system. They are administered via injection or infusion and have shown significant efficacy in reducing symptoms for many patients.
Chart of Treatment Options
| Treatment Type | Examples | Effectiveness | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topical | Corticosteroids, Vitamin D Analogues | High for mild to moderate cases | Best for localized treatment |
| Phototherapy | UVB, PUVA, Excimer Laser | Very effective for moderate to severe cases | Requires medical supervision |
| Systemic | Oral Retinoids, Immunosuppressants, Biologics | High for severe cases | May have significant side effects |
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to medical treatments, certain lifestyle changes can help manage psoriasis symptoms. These include:
- Healthy Diet: Eating an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help reduce flare-ups.
- Stress Management: Stress is a known trigger for psoriasis, so practices like yoga, meditation, and mindfulness can be beneficial.
- Moisturizing: Keeping the skin moisturized can help prevent dryness and scaling, making it easier to manage symptoms.
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding personal triggers such as alcohol, smoking, and certain medications can help reduce flare-ups.
Conclusion
Managing psoriasis can be challenging, but understanding the different treatment options available empowers patients to make informed decisions. Whether through topical treatments, phototherapy, or systemic medications, there are effective ways to control symptoms and improve quality of life. Always consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action tailored to individual needs.